In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use Kotlin’s forEach higher-order function.
When we need to iterate over an array or list to search for or filter specific data, the traditional for loop is often used. However, in Kotlin, there’s a more functional and concise approach—the forEach function.
Let’s create a simple example using forEach.
Simple forEach Example in Kotlin
val list = listOf(1, 2, 3)
list.forEach { item ->
println(item)
}

- In this example, the listOf function creates a simple list.
- using the forEach function, each item will be iterated.
- The it keyword is used for the current item. In the first iteration, it contains the value 1, in the second iteration, it becomes 2, and in the final iteration, it holds the value 3.
- Each value prints to the terminal
Contents
Range with forEach
In this part, we can use range with forEach. In kotlin, range means sequence of values defined between start value and end value.
Sometimes, you don’t need to create a list. You can use a range directly like below, which is more memory-efficient.
(1..3).forEach {
println(it)
}

- Above, we have a range that contains the values 1,2, and 3.
- Each element is printed in the terminal one by one.
Using forEach with a string
If you’re a beginner, you may encounter coding questions in interviews such as counting characters in a string. in these situations, forEach function can be quite useful.
val charArray = "String"
charArray.forEach {
println(it)
}
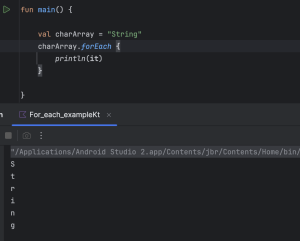
- In this section, forEach treats String as character array. So each character in string will be iterated over.
Using forEach with array
val array = arrayOf("a","b","c")
array.forEach {
println("array : $it")
}
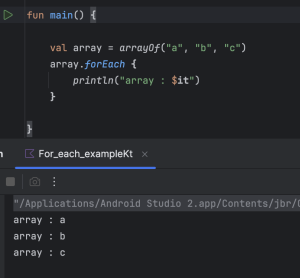
- Just like list, we can use array.
- it is the current item.
Using forEach with Maps
val map = mapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c")
map.forEach{ (key, value) ->
println("Key: $key -> Value: $value")
}

- In this case, mapOf create a simple map, making numbers 1, 2, and 3 the keys and “a”, “b”, and “c” the values.
- Unlike lists, when you use forEach with maps, the lambda expression provides the key and value as parameters.
- This allows you to display your data effectively.
Using forEachIndexed with list
forEach, which comes with an index, is called forEachIndexed.
If you are creating a list and need to display each item with its index, you can use this higher-order function.
val list = listOf(1, 2, 3)
list.forEachIndexed { index, item ->
println("Index: $index, Item: $item")
}
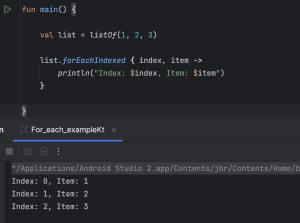
- This part, you will receive index along with item.
- If you don’t need index, simply use forEach.
Using forEachIndexed with map
val map = mapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c")
map.entries.forEachIndexed{ index, item ->
println("Index: $index, Key: ${item.key} -> Value: ${item.value}")
}
- You can’t directly use forEachIndexed on a map.
- Like shown above, you need to use entries property to get a set of key/value pairs from map.
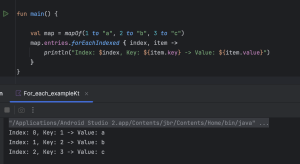
forEach – continue functionality
You can use continue statement directly in a for loop, but you cannot use it directly in forEach.
val list = listOf(1, 2, 3)
list.forEach {
if(it==2){
println("Skips the second iteration")
return@forEach
}
println(it)
}

- Use return@forEach to stop the current iteration and continue with the next one in the loop.
forEach – break functionality
val list = listOf(1, 2, 3)
run loop@{
list.forEach {
if(it==2){
println("Skips iterations from here")
return@loop
}
println(it)
}
}
- Use return@loop break out of the forEach loop.
Complete Source Code
package com.androidride.kotlin
fun main() {
val list = listOf(1, 2, 3)
println("simple list - forEach example")
list.forEach {
println(it)
}
println("range with foreach")
(1..3).forEach {
println(it)
}
println("string with foreach")
val charArray = "String"
charArray.forEach {
println(it)
}
println("array with foreach")
val array = arrayOf("a","b","c")
array.forEach {
println("array : $it")
}
println("map with foreach")
val map = mapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c")
map.forEach{ (key, value) ->
println("Key: $key -> Value: $value")
}
println("forEachIndexed with lists")
list.forEachIndexed { index, item ->
println("Index: $index, Item: $item")
}
println("forEachIndexed with maps")
map.entries.forEachIndexed{ index, item ->
println("Index: $index, Key: ${item.key} -> Value: ${item.value}")
}
println("forEach - break functionality")
run loop@{
list.forEach {
if(it==2){
println("Skips iterations from here")
return@loop
}
println(it)
}
}
println("forEach - continue functionality")
list.forEach {
if(it==2){
println("Skips the second iteration")
return@forEach
}
println(it)
}
}